The Static Units System in Ptolemy II provides the means to constrain a model in terms of the allowable units of measure for the actors, and ports on the actors. It is static, in that the constraints do not relevant when the model is run. Rather, the constraints are used to determine if the model is correct.
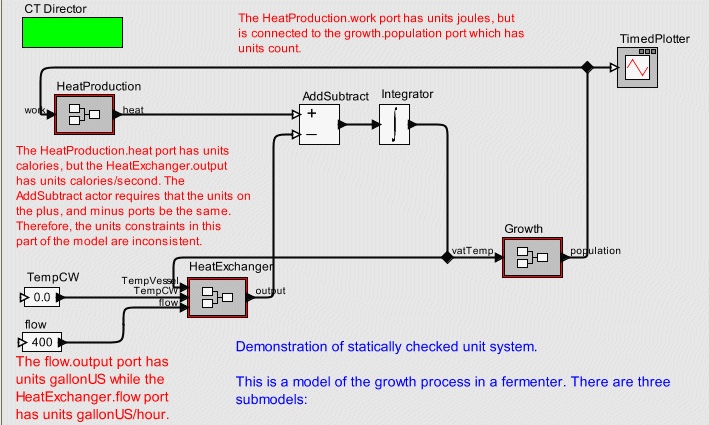
In order to illustrate these concepts, the Fermenter model, shown here, will be used.

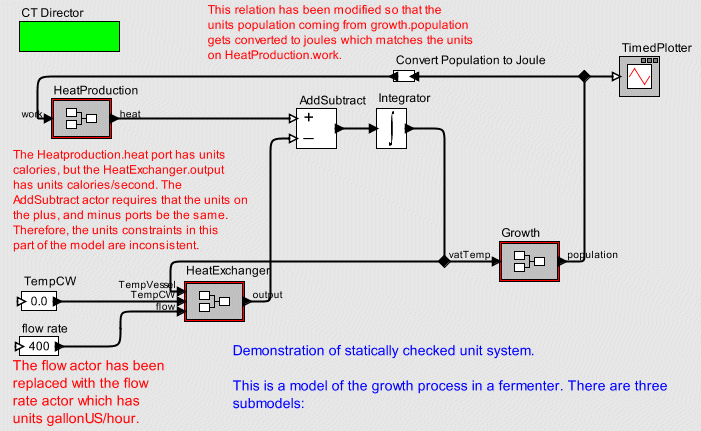
The purpose of this model is simulate the growth process in a fermenter. There are three submodels; 1) growth models the number of cells being produced as a function of the current number of cells and the vat temperature, 2) HeatProduction models the amount of heat produced (in calories) as a function of the amount of work done (in joules), and 3) HeatExchanger models the removal of heat from the vat as a function of the rate at which water flows through the cooling jacket around the vat.
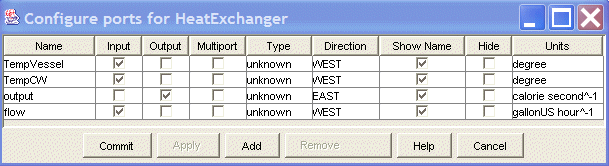
Note the units column which shows that, the TempVessel port has units degree, the TempCW port has units degree, the output port has units calories/second, and, the flow port has units gallons/hour.
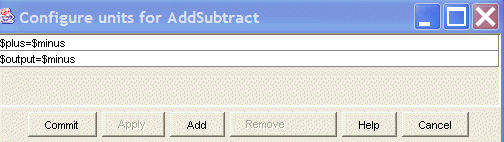
This shows that there are two units constraints for the AddSubtract actor. The expression $plus=$minus says that the plus and minus ports must have the same units. For example, it is incorrect to subtract gallons/hour from gallons. Similarly, the expression $output=$minus says that the output port must have the same units as the minus port.
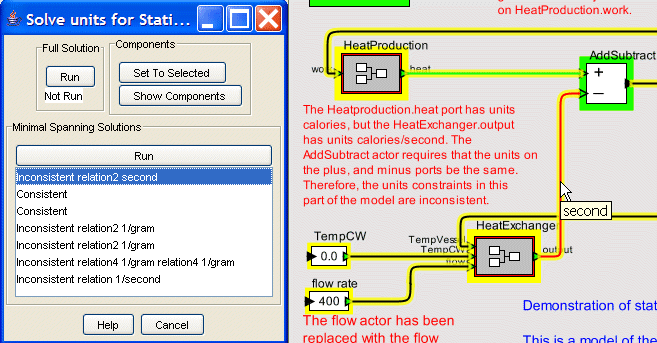
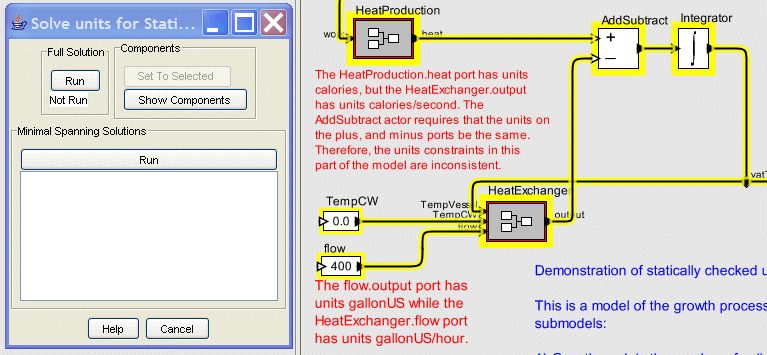
Some of the units constraints in the model are inconsistent. In addition to the HeatExchanger port unit constraints, and AddSubtract actor unit constraints illustrated above, the HeatProduction.heat port has the units calories. Since the HeatProduction.heat port is connected (via the AddSubtract actor) to the HeatExchanger.output port which has units calories/second the model is inconsistent in terms of the units constraints.
The UnitConstraint Solver is used to discover, analyze, and, in some cases, fix, unit inconsistencies that exist in a model. The UnitConstraintSolver Dialog is a user interface tool that provides an interface to the UnitConstraints Solver. For a detailed reference explanation of just the UnitConstraints Solver Dialog, click here.
To start the UnitConstraint Solver right mouse-click and select UnitsConstraint Solver as shown below.
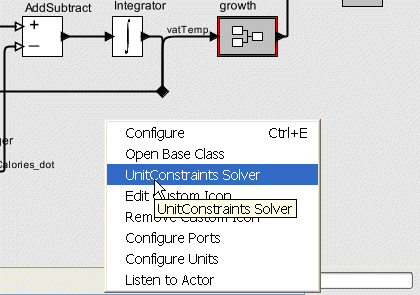
This will cause the UnitConstraints Solver Dialog to appear as shown below. Although, no components were selected prior to starting the UnitConstraintsSolver Dialog it is assumed that all of the components will be used. A component is highlighted with yellow if it is a member of this set.
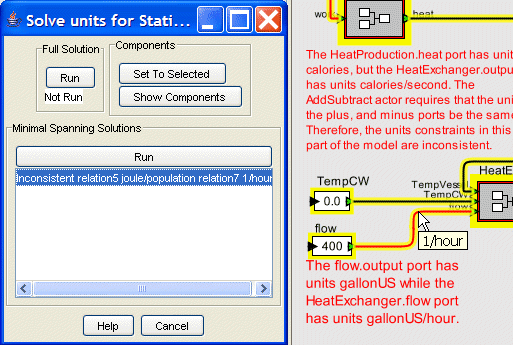
This is indicated in the results pane with the label Inconsistent relation5 joule/population relation7 1/hour. This is a shortened version of the results and indicates three properties
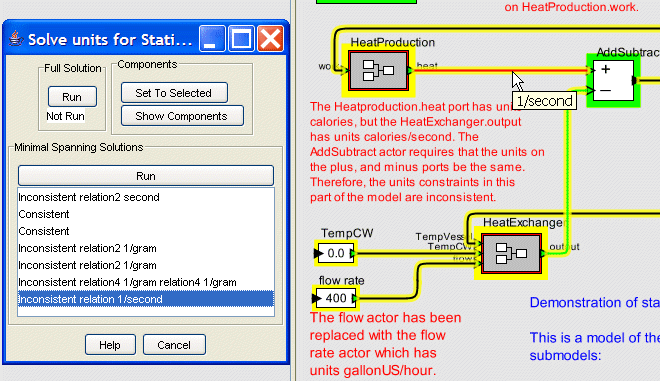
If the result Inconsistent relation5 joule/population relation7 1/hour is selected the result is then displayed in the graph viewer. The components that are part of the minimal span solution are colored with green signifying that a component is consistent and red signifying that it is inconsistent. In the above graphic, relation7 connects the flow actor to the HeaExchanger actor with flow.output having units gallonUS, and HeatExchanger.flow having units gallonUS/hour. This relation is red indicating that it is inconsistent. In addition, the graphic also shows that if the cursor is placed over the relation on the graph viewer the requisite transformation 1/hour is displayed as a tooltip.
The graph viewer also displays the inconsistency found on relation5 (this is in a portion of the graph viewer not shown in the above graphic). In this case the growth.population port has units population and is connedted (via relation5) to the HeatProduction.work port that has units joules. Placing the cursor over this relation causes the tooltip joule/population to appear.
These changes have been implemented in the model StaticUnits2.xml which is located in the same directory as StaticUnits.xml used above. Click here to start it. The following graphic shows these changes.
The following graphics illustrate these situations.