Configuring Ports
The Configure Ports dialog supports adding, removing, and changing key
properties of ports of an entity.
It displays the ports of an actor in tabular form with each row representing a port
and each column a particular property of a port.
An example is shown below:
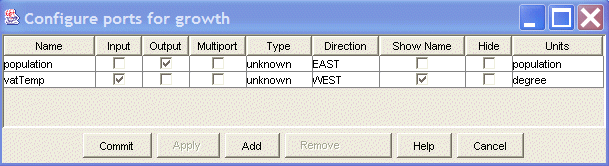
Editing a cell does not immedialtely cause the corresponding port property to be changed.
Pressing the Apply button will cause any modifications of the table to be applied to
the port properties.
Pressing the Commit button causes the dialog to be dismissed after any table modifications
are applied.
Pressing the Cancel button causes any pending table modifications to be discarded and
the dialog to be dismissed.
Editing Port Properties
For the most part, editing the port properties is straight forward.
Just click in the
cell to be edited and an obvious interaction will ensue.
Some properties may not be editable because they are part of a class definition and, are,
therfore immutable.
These cells will have a red background (e.g.
 ) and will ignore any attempts at editing.
) and will ignore any attempts at editing.
Name - Names must not contain a period, must be non-blank, and must be unique.
Input, Output, Multiport - Checkboxes that determine if a port is input, output, or both.
Type - The type can be given by any expression that can be evaluated
(this expression is called a "prototype").
For example, you can specify the type to be double by giving
the string "0.0" (or any other number with a decimal point).
However, this does not look very good as
a designator for a type. The Ptolemy II expression language
defines the constant "double" to equal "0.0". Thus, the preferred
way to specify that a port has type double is to give its type
as "double".
The primitive types you might specify are:
- boolean,
- complex,
- double,
- fixedpoint,
- general,
- int,
- long,
- matrix,
- object,
- scalar,
- string, and
- unknown.
The constant "unknown" has a rather special behavior, in that
it sets the type of the port to be unknown, allowing type resolution
to infer it. The constant "matrix" designates a matrix
without specifying an element type, in contrast to, for example,
"[double]", which specifies a double matrix (see below).
Similarly, the constant "scalar" designates a scalar of any type
(double, int, long, etc.).
The constant "general" designates any type.
Since the type is given by a "prototype",
any data type that can be given in an expression
can be specified as a type. For structured types, follow the
same syntax as in expressions. For example:
{double} - double array
[int] - int matrix
{field1 = string, field2 = int} - record with two fields
Direction - The Cardinal Direction determines which side of the icon the
port is located on.
Clicking in this cell brings up a menu that provides the means to select a specific side, i.e.
NORTH, EAST, SOUTH, WEST.
DEFAULT can also be selected.
Below are the defaults:
- Input ports are usually on the West side.
- Output ports are usually on the East side.
- Ports that are both an input and an output are located on the South side.
Show Name - Checking this box will cause the name of the port to be displayed.
Unchecking it will remove the name from the display.
Hide - Checking this box will cause the port to be displayed.
Unchecking it will cause remove the port from the display.
Units - The units specification for the port.
Adding a port
To add a port, click on the Add button.
This will add a new row with either default, or unspecified cells.
Edit the cells as required for the new port.
Removing ports
Select the row that contains the port to be removed.
On a Windows platform selecting a row is accomplished with a right-mouse click in the row.
On a Mac platform selecting a row is accomplished with a command-click in the row.
When a row is selected the name of the port will be displayed in the Remove button.
Pressing the Remove button will remove the port from the table.


 ) and will ignore any attempts at editing.
) and will ignore any attempts at editing.